Advanced storage mappings considering tiers and redundancy
Storage is a main cost factor to be considered when laying out a plan for a cloud migration. First, collecting and assessing storage always needs to consider expected growth rates. But usage patterns and access performance are also parameters to be considered for successful application deployments with optimized costs.
Storage offerings by disk type
All major cloud service providers (CSP) offer similar disk and storage options. Those options are common (but not all) selection criteria and listed below:
Disk types and storage tiers:
- SSD for overall better performance versus HDD for cost-effectiveness
- Storage (performance) tiers, particularly related to IO performance (typical or guaranteed IOPS)
The below table compares storage offerings by disk type and maximum performance across the CSPs.
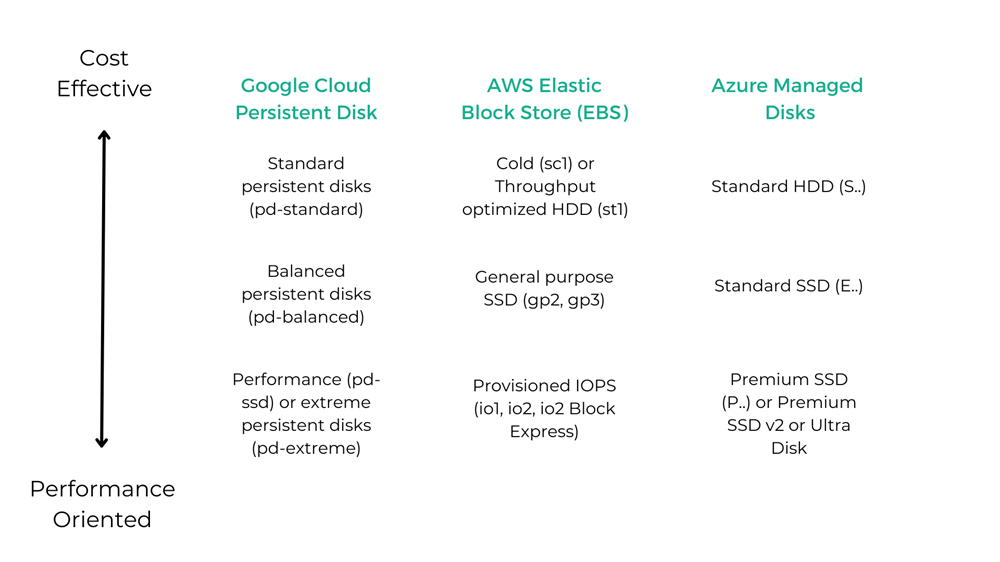
Note that this comparison only considers ranges of disk performances as different VM configurations, the shape and number of IO operations, disk size, etc. usually require a more detailed analysis for a side-by-side comparison. Also, some types of block storage are not listed in the table: e.g. Google Cloud's Hyperdisk - a distributed network storage option, boot disks or local disks - typically ephemeral i.e. non-durable block storage for temporary or low-value data.
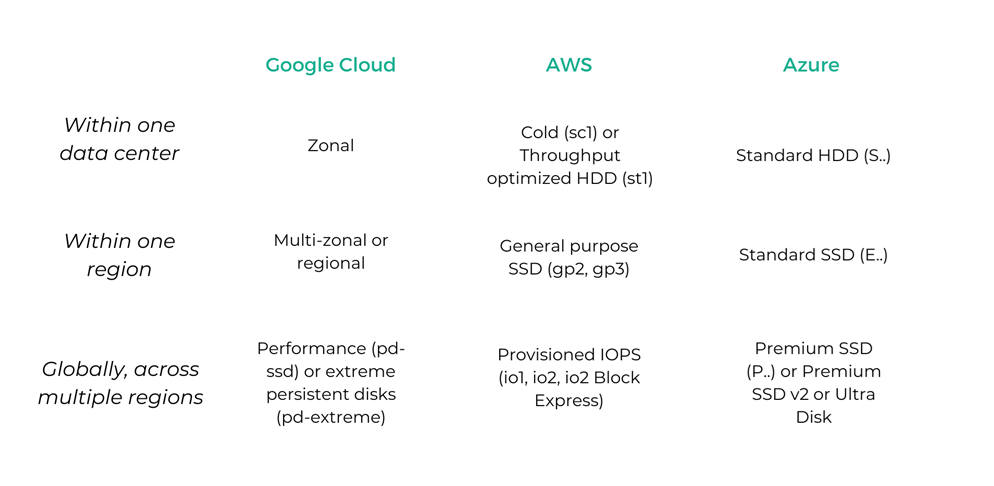
Redundancy options via live disk replication to prepare against drive failures or entire data center outages.
The below comparison shows replication options and the typical naming for those options across the CSPs.
 Corresponding custom machine type mappings in Txture for on-premises VMs of different sizing.
Corresponding custom machine type mappings in Txture for on-premises VMs of different sizing.
Note that this comparison looks at disk storage only, although it lists some options for higher-tier redundancy. If you only look into snapshots and data replication outside of live volumes you have more options.
Fixed-size disks or flexible disk sizing
Depending on disk types and storage tiers the CSPs have different minimum disk sizes that one can use. Usually, disk sizes can be configured in the precision of 1GB increments, except for Azure Managed disks where disk sizes follow power-of-2 sequence in GBs (4, 8, 16, …, 4096, …) - with the notable exception of the "v2" types that also offer 1GB increments.
There are many more characteristics describing features of cloud disk storage, like disks being usable as boot disks, volumes that can be attached to multiple VMs, backup/DR and snapshot options, etc. but we won't go into those details in this article.
Now with the newly improved cloud storage mapping functionality, Txture considers the above-described criteria and automatically picks the right disks for your application servers. You can either express it in Txture's target architecture preferences if you have specific disk requirements in mind for your entire application portfolio or some applications. You can also let Txture identify your existing cloud storage products and map them to a corresponding storage product of a different CSP in a business case building exercise.
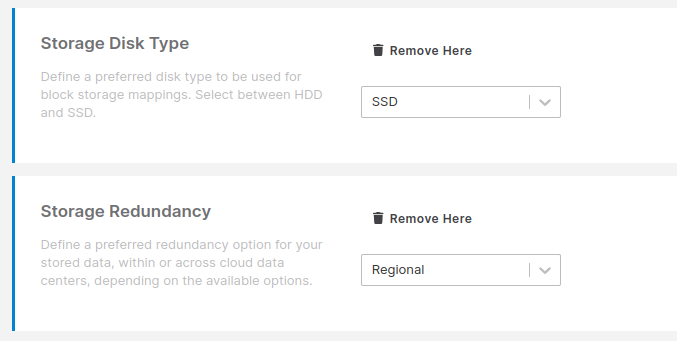 Txture's target architecture preferences to manually define your cloud strategy for server disks of your business applications.
Txture's target architecture preferences to manually define your cloud strategy for server disks of your business applications.
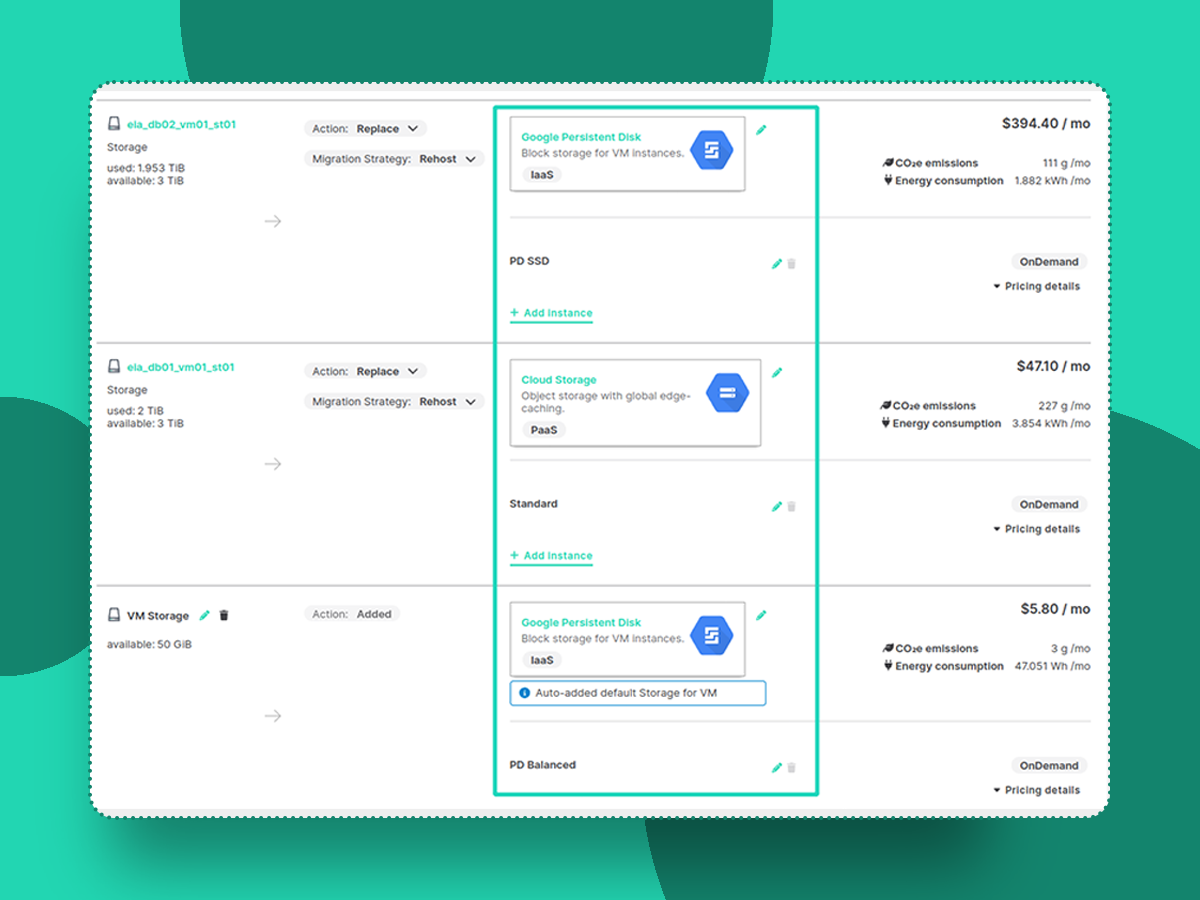
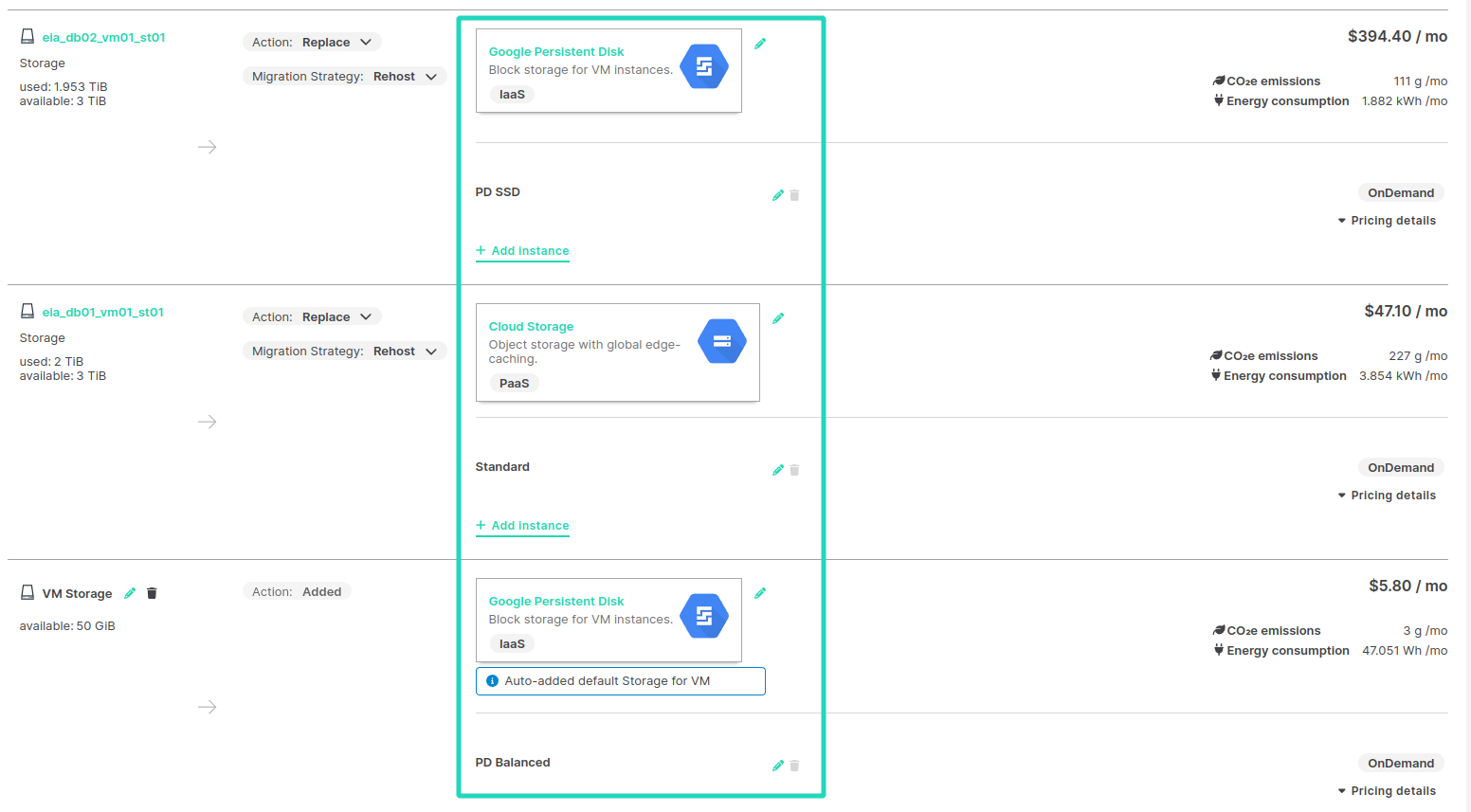 An application BOM listing different disk storage types that depend on on-premises disk types and defined cloud storage mapping preferences.
An application BOM listing different disk storage types that depend on on-premises disk types and defined cloud storage mapping preferences.
Txture is a cloud knowledge company. We continue to strive for detailed assessments of cloud and on-premises landscapes and optimal cloud target architectures, boosting your cloud transformation initiatives with automation and clarity.
Some references to the different disk storages for the major CSPs:
Your feedback to our new feature
Want to learn more about Txture's capabilities for your cloud transformation? Reach out to us, we'll be happy to help!