Green Cloud: 4 things Cloud Providers do to be more sustainable

In this article, we'll explain what green cloud actually means and show you four steps that providers take to be more sustainable. In the end, we will show you how to effectively reduce your IT's carbon footprint, by making green factors an essential part of your cloud strategy.
What does "green cloud" mean?
The term green cloud refers to a sustainable way of cloud computing: reducing energy demand and saving money, while keeping an eye on environmental issues. Moving traditional IT landscapes to the cloud per se can come with beneficial elements for the environment like e.g. reduced amount of physical servers and land coverage or increased average utilization of available computing units. But if Cloud Providers do it right, a measurable impact on a company’s CO2 footprint can be achieved.
“Green cloud" has become a buzzword, as more companies are now taking into account the CO2 emissions and the overall carbon footprint of their new cloud service providers' facilities when planning their cloud migration. Respectively, sustainability is becoming a main point of differentiation in the marketplace, both for global hyperscalers like AWS, Google Cloud or Microsoft Azure and for European cloud companies like OVH.
4 things Cloud Providers do to be more sustainable
Aligned with both the climate crisis and rising energy costs, cloud service providers are putting all their efforts in shifting their services to be more environmentally friendly. A big step towards sustainable cloud computing is efficiency improvement especially regarding physical data centers. These four target efforts are leading into a future of greener cloud services:
1 - Strategic data center locations
 Choosing the right datacenter location can limit energy consumption
Choosing the right datacenter location can limit energy consumption
The operation of a data center requires loads of energy. While the majority of this energy is needed to power the servers, a big part also goes into cooling them to protect the equipment. If data center locations are picked strategically, their power demand can be substantially reduced: data centers that are located in cool regions (such as Finland or Sweden) or in underground facilities, need much less cooling compared to locations in e.g. desertic or subtropical regions like in the Southern US.
There are also innovative recycling concepts that use the waste heat produced in the cooling process to heat nearby homes and businesses.
2 - Usage of green energy
 The use of green energy is a central aspect of sustainable cloud computing
The use of green energy is a central aspect of sustainable cloud computing
The use of green energy, coming from sustainable sources, is a central part to sustainable cloud computing. Many Cloud service providers are following the global demand for more sustainability and adjust their energy sources:
- Wind energy
- Solar energy
- Water craft (if available)
- Incorporation of big battery banks to store the green and more discontinuous energy
The availability of green energy resources is of course linked to the strategic choice of location described above. The higher the usage rate of green energy, the lower the share of CO² intense energy forms such as coal or gas.
3 - Energy-efficient hardware
 Cloud providers use energy-saving strategies for their hardware infrastructure
Cloud providers use energy-saving strategies for their hardware infrastructure
To reduce the overall need of energy in data centers, cloud providers strive to use optimized and modern hardware and software infrastructure. That does not limit to changing the old light bulbs to energy-saving lights!
Data centers employ energy-saving strategies such as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) or shifting to modern data storage devices: SSDs (as compared to their legacy technology HDDs) need less power, access data faster and even last longer until replacement. Through the use of optimized hardware, data centers become more efficient and also minimize their energy demand.
4 - Shifting workloads
To distribute the maximum load required of a data center, providers try to shift non-time critical workloads to different times slots to reduce the overall network traffic. That way, data centers avoid peak times. That’s what everybody does, if they have to take the car or bus to the city center: some appointments have fixed times and leave no choice. But if time is not an issue, people tend to avoid the rush hours’ traffic jams and overcrowded buses.
Efficiently reduce your carbon footprint with the Txture platform
A lot of organizations struggle to get a good understanding of their IT carbon footprint, and to make the right choices for sustainability.
Txture's SaaS platform is used by cloud governance teams and sustainability leaders to get a complete overview of their current carbon footprint, and get the right recommendations to effectively reduce it.
Understand the current carbon footprint associated with your cloud portfolio
With Txture, you quickly develop a complete overview of the carbon footprint associated with your IT portfolio. The carbon footprint can be analyzed from a wide variety of angles. For instance, per application, business unit, deployment location, or cloud provider.
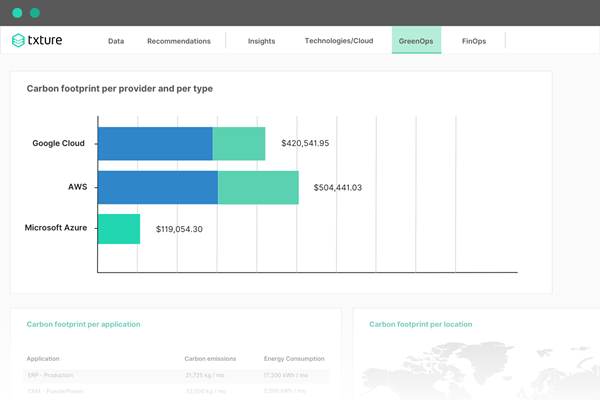 Analyze your current IT's carbon footprint from a wide variety of angles
Analyze your current IT's carbon footprint from a wide variety of angles
See where you can optimize and modernize to reduce your carbon footprint
Through an analysis of your application portfolio, the platform automatically provides actionable recommendations to lower your carbon footprint.
It can be, for instance, moving specific workloads to another deployment location, or right-size some of your applications. The recommendations depend on your strategy regarding cloud modernization and sustainability goals.
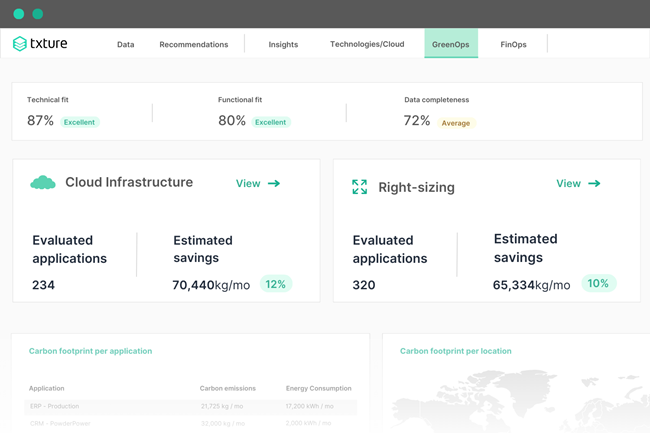 Get automated, actionable recommendations to start reducing your carbon footprint
Get automated, actionable recommendations to start reducing your carbon footprint
Track the impact of optimization over time
Sustainability is one factor that needs to be considered along with other goals, such as cost optimization, security, or technology modernization.
Txture gives you recommendations on all these dimensions, and let you track the evolution of the indicators that are most important to you.
See the impact of cloud optimization on costs, carbon footprint reduction and business/technical fit!
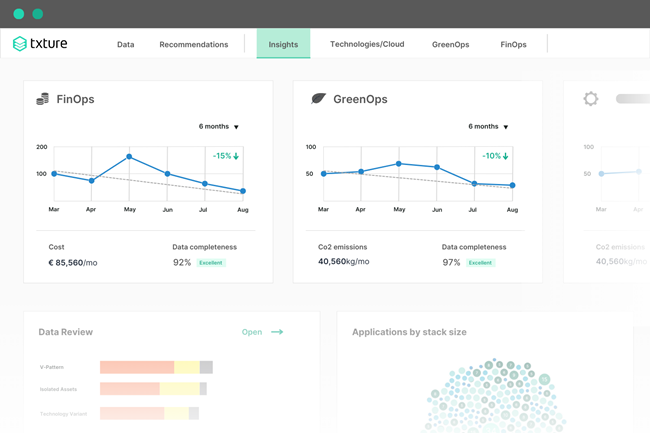 Track the impact of your optimization initiatives on cost and carbon footprint reduction
Track the impact of your optimization initiatives on cost and carbon footprint reduction
In a nutshell, Txture helps you to integrate the sustainability factor in your decision-making, and prioritize initiatives that will effectively reduce the carbon footprint associated with your application portfolio.
Seeing is believing!
Learn more about Txture's capabilities to reduce your IT carbon footprint.
Get started now - Our team will be happy to give you a first demo and answer your questions about the Txture Platform!
